Operates a two-stage data treatment process, based on two data treatment functions, and a pass/fail
function which detects outliers. This function is set up to allow any functions to be passed as the
data treatment functions (f1 and f2), as well as any function to be passed as the outlier detection
function f_pass.
Usage
# S3 method for class 'numeric'
Treat(
x,
f1,
f1_para = NULL,
f2 = NULL,
f2_para = NULL,
f_pass,
f_pass_para = NULL,
combine_treat = FALSE,
...
)Arguments
- x
A numeric vector.
- f1
First stage data treatment function e.g. as a string.
- f1_para
First stage data treatment function parameters as a named list.
- f2
First stage data treatment function as a string.
- f2_para
First stage data treatment function parameters as a named list.
- f_pass
A string specifying an outlier detection function - see details. Default
"check_SkewKurt"- f_pass_para
Any further arguments to pass to
f_pass(), as a named list.- combine_treat
By default, if
f1fails to passf_pass, thenf2is applied to the originalx, rather than the treated output off1. Ifcombine_treat = TRUE,f2will instead be applied to the output off1, so the two treatments will be combined.- ...
arguments passed to or from other methods.
Details
The arrangement of this function is inspired by a fairly standard data treatment process applied to indicators, which consists of checking skew and kurtosis, then if the criteria are not met, applying Winsorisation up to a specified limit. Then if Winsorisation still does not bring skew and kurtosis within limits, applying a nonlinear transformation such as log or Box-Cox.
This function generalises this process by using the following general steps:
Check if variable passes or fails using
f_passIf
f_passreturnsFALSE, applyf1, else returnxunmodifiedCheck again using *
f_passIf
f_passstill returnsFALSE, applyf2(by default to the originalx, seecombine_treatparameter)Return the modified
xas well as other information.
For the "typical" case described above f1 is a Winsorisation function, f2 is a nonlinear transformation
and f_pass is a skew and kurtosis check. Parameters can be passed to each of these three functions in
a named list, for example to specify a maximum number of points to Winsorise, or Box-Cox parameters, or anything
else. The constraints are that:
All of
f1,f2andf_passmust follow the formatfunction(x, f_para), wherexis a numerical vector, andf_parais a list of other function parameters to be passed to the function, which is specified byf1_paraforf1and similarly for the other functions. If the function has no parameters other thanx, thenf_paracan be omitted.f1andf2should return either a list with.$xas the modified numerical vector, and any other information to be attached to the list, OR, simplyxas the only output.f_passmust return a logical value, whereTRUEindicates that thexpasses the criteria (and therefore doesn't need any (more) treatment), andFALSEmeans that it fails to meet the criteria.
See also vignette("treat").
Examples
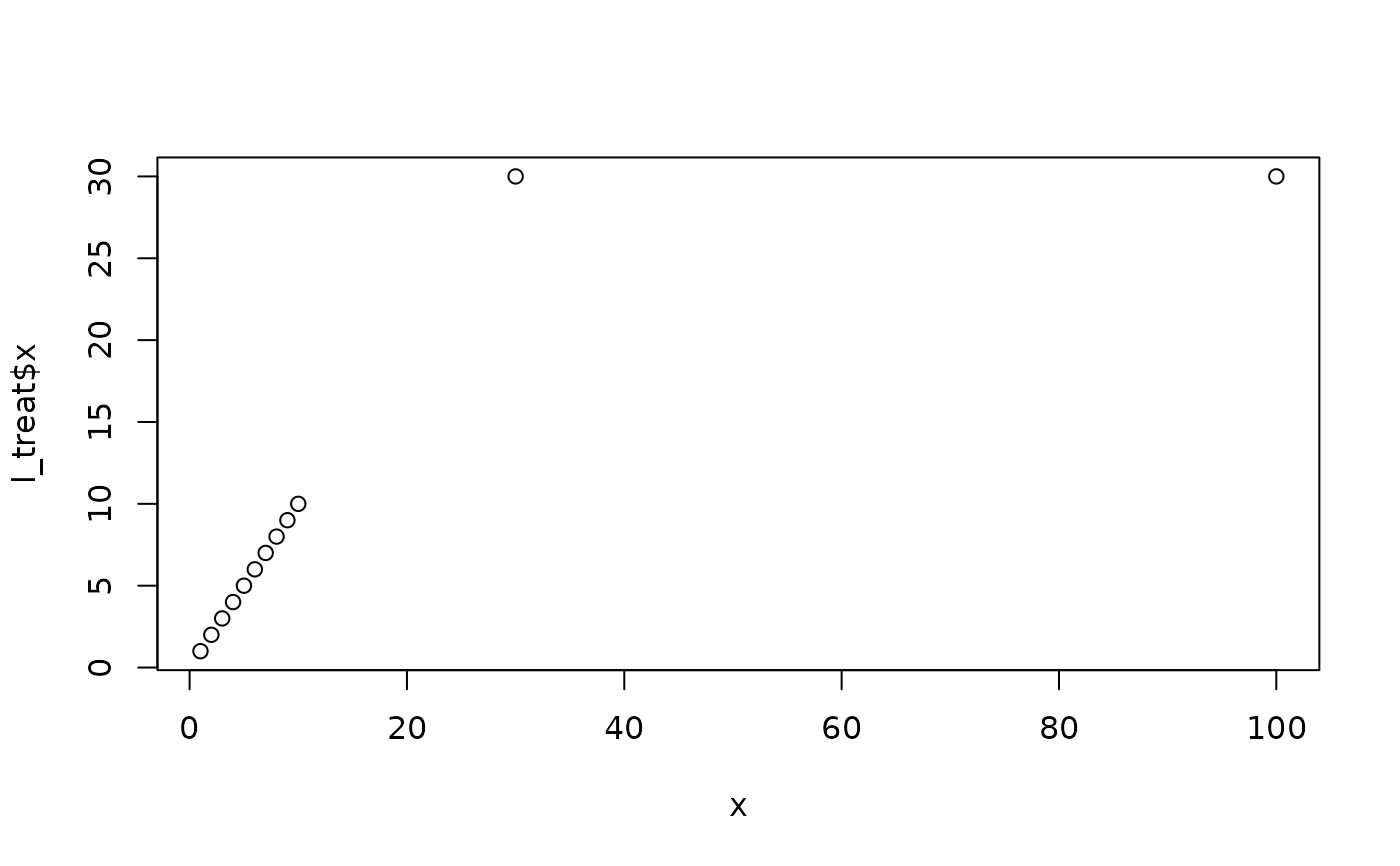
# numbers between 1 and 10
x <- 1:10
# two outliers
x <- c(x, 30, 100)
# check whether passes skew/kurt test
check_SkewKurt(x)
#> $Pass
#> [1] FALSE
#>
#> $Skew
#> [1] 3.063241
#>
#> $Kurt
#> [1] 9.741391
#>
# treat using winsorisation
l_treat <- Treat(x, f1 = "winsorise", f1_para = list(winmax = 2),
f_pass = "check_SkewKurt")
# plot original against treated
plot(x, l_treat$x)